What is software security and why it matters today

Team Fueler
05 Nov, 2025

Software security protects applications from unauthorized access, data theft, and exploitation. As modern software increasingly relies on open source code, APIs, and cloud infrastructure, the attack surface has greatly expanded.
So, in this guide, we’ll explain what software security is, how it works, and why your organization needs it today.
What is software security?
Software security protects software applications from malicious attacks and data breaches throughout their entire software development life cycle.
It involves identifying security vulnerabilities early, writing secure code, and testing for weaknesses before deployment. Security teams integrate security engineering directly into the development process instead of treating it as an afterthought. For example, they apply static and dynamic application security testing to uncover risks during coding and QA stages.
In other words, software security focuses on building software systems that defend sensitive data, maintain reliability, and comply with security best practices from day one.
Specifically, it consists of:
- Building secure software through secure coding and threat modeling
- Performing static and dynamic application security testing
- Managing vulnerabilities and patching third-party components
- Conducting regular security audits and code reviews
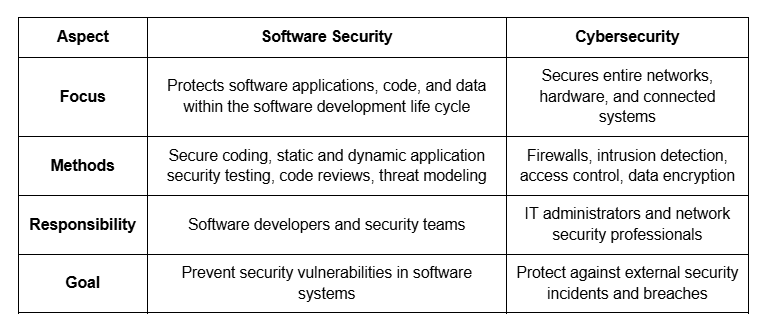
Software security vs Cybersecurity
Software security and cybersecurity often overlap, but they target different layers of protection.
Let’s compare how they differ in scope and methods:
How does software security work?
Software security works through structured processes that integrate protection into every stage of the software development life cycle. You have to build secure software by combining testing, monitoring, and continuous improvement rather than treating security as a final step.
Here’s how the process works step by step:
- Design phase. Security teams analyze system vulnerabilities, define access control, and plan secure coding practices.
- Development phase. Developers apply secure software development techniques such as code reviews and threat modeling.
- Testing phase. Teams perform static and dynamic application security testing to detect weaknesses.
- Deployment phase. Security audits and penetration testing confirm that applications meet compliance standards. Cloud infrastructure plays a major role in software resilience and compliance. Partnering with one of the best cloud consulting companies, such as Future Processing, helps organizations design secure architectures that limit vulnerabilities and maintain operational efficiency.
- Maintenance phase. Regular updates and monitoring protect against software supply chain attacks and new security risks.
Why is software security important today?
Software security protects organizations from financial loss, data breaches, and operational disruption. Modern software depends on third-party components, APIs, and cloud services, which expand the attack surface. Attackers target vulnerable software systems to access sensitive data or install malicious code. In 2025, software supply chain attacks and identity theft have become major risks across industries.
Strong software security practices help companies maintain compliance with regulations such as GDPR and the EU Cyber Resilience Act. Security software also supports risk management and keeps software systems reliable. For example, a single unpatched vulnerability can expose millions of users and damage brand trust.
Software security matters today because it:
- protects sensitive data from theft, misuse, or exposure during software operations.
- prevents financial and reputational damage caused by security breaches or ransomware attacks.
- helps organizations comply with global regulations such as GDPR and the EU Cyber Resilience Act.
- reduces risks from third-party components and software supply chain attacks.
- strengthens business continuity by keeping software systems stable and available.
- builds user confidence through transparent and secure software development practices.
Software security techniques and best practices
Software security techniques protect software applications at every stage of the software development life cycle. Let's break down each method.
1. Secure coding
Secure coding forms the foundation of strong software security. You can write code that prevents security vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or insecure authentication. Simple habits – like validating input, managing errors correctly, and limiting privileges – reduce the chance of exploitation.
2. Application security testing
Application security testing helps you understand how software behaves under different attack scenarios. Static application security testing checks the source code before it runs, while dynamic application security testing evaluates live applications. Using both methods can help you identify security vulnerabilities before release.
3. Access control and data protection
Access control restricts who can view or modify software systems. Strong access control policies are a core part of data protection and help organizations keep sensitive information secure. You can add multi factor authentication, enforce strong passwords, and use data encryption to protect sensitive information. These software security measures reduce the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access.
4. Continuous monitoring and security audits
Continuous monitoring allows you to detect suspicious activity or potential security incidents in real time. Regular security audits confirm that your systems comply with internal policies and industry regulations. You can also use automated event management tools to review logs, track vulnerabilities, and improve software security over time.
Conclusion
Software security protects software systems from security vulnerabilities, data breaches, and malicious attacks that threaten business operations.
You can improve software security by integrating secure coding, application security testing, and continuous monitoring throughout the software development life cycle. These practices help prevent security incidents, protect sensitive data, and maintain compliance with international standards such as GDPR.
Key takeaways:
- Software security focuses on building secure software from design to deployment.
- Strong software security measures support data protection and user trust.
- Continuous testing and security audits reduce long-term security risks.
FAQs
1. What is software security?
Software security is the process of designing, developing, and maintaining software applications that resist security threats and protect sensitive data. It focuses on identifying vulnerabilities early in the software development life cycle. Developers use secure coding, code reviews, and security testing to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious attacks. The goal is to create software systems that remain safe and reliable under real-world conditions.
2. How does software security differ from cybersecurity?
Software security focuses on protecting software applications and code from exploitation. Cybersecurity covers broader protection of computer systems, networks, and data infrastructure. In other words, cybersecurity secures the external environment, while software security safeguards the internal structure of applications. Both disciplines work together to prevent security incidents and maintain information security.
3. What are the main types of software security?
The three main types are application security, network security, and cloud security. Application security protects the software itself through secure coding and testing. Network security manages firewalls, access control, and encryption. Cloud security focuses on protecting data and workloads within virtual environments. Each type complements the others to reduce overall security risks.
4. How does software security work in the development process?
Software security operates through structured stages in the software development life cycle. Security teams define requirements, apply secure coding practices, and conduct static and dynamic application security testing. Continuous monitoring and regular security audits detect and resolve new vulnerabilities. Integrating security into development workflows helps prevent future security breaches.
5. What are examples of software security tools?
Common software security tools include static application security testing (SAST) tools like SonarQube, dynamic application security testing (DAST) tools such as OWASP ZAP, and vulnerability scanners like Nessus. You can also use code review platforms, penetration testing tools, and access management systems to detect and fix security flaws during development.
What is Fueler Portfolio?
Fueler is a career portfolio platform that helps companies find the best talent for their organization based on their proof of work. You can create your portfolio on Fueler, thousands of freelancers around the world use Fueler to create their professional-looking portfolios and become financially independent. Discover inspiration for your portfolio
Sign up for free on Fueler or get in touch to learn more.